Fail Over
In contrast to load balancing, fail over operation requires that the system is accessible at all times. However, usually only one server is primarily used for requests. If this server fails, the second server is used and the end user does not notice the failure.
A keep-alive service ensures that the load distributor is notified if a system failure occurs. This allows to immediately switch over to the second server.
Scenario – A Single Exclusive Database
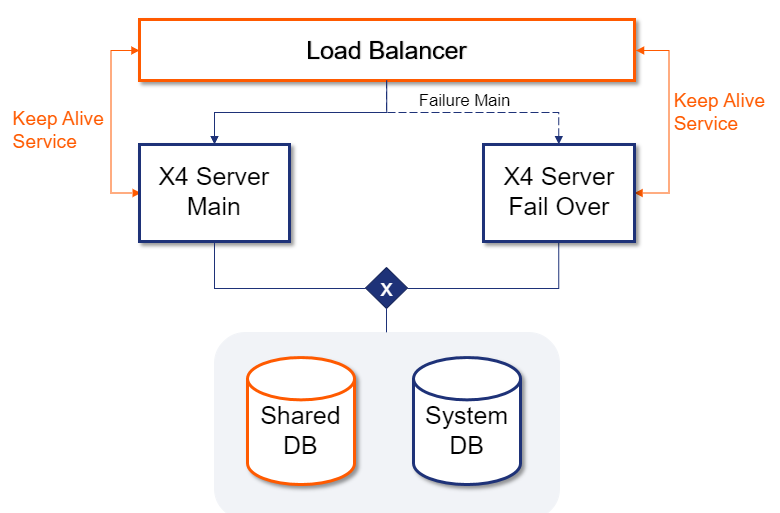
Figure: A single database with exclusive access
The simplest system contains two X4 Server instances that can receive both requests. A single database is used for both servers. Thus, for data integrity it is important that only one of the two servers has access to the database at a time.
Scheduled services can be implemented using an external scheduler or a logical lock on a table of the shared database Shared DB.
Scenario – System Database per X4 Server
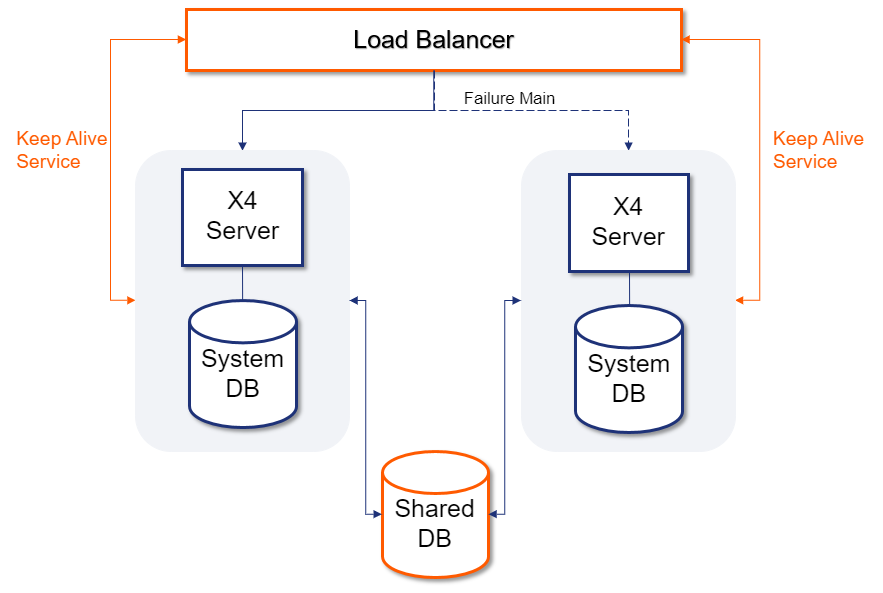
Figure: Separate system databases
If load balancing and fail over are to be provided through the system structure, each X4 Server requires its own system database. This allows each X4 Server to respond to requests. If only ail over is to be ensured, all requests are redirected to only one of the two X4 Servers.
Scheduled services can be implemented using an external scheduler or a logical lock on a table of the shared database Shared DB.
